Introduction:
Sand casting is a versatile and widely usedsand casting parts process for producing complex metal parts. It is one of the oldest and most economical methods for manufacturing parts, dating back thousands of years. This question aims to explore the sand casting process in detail, from its basic principles to its applications in modern manufacturing.
Understanding Sand Casting:
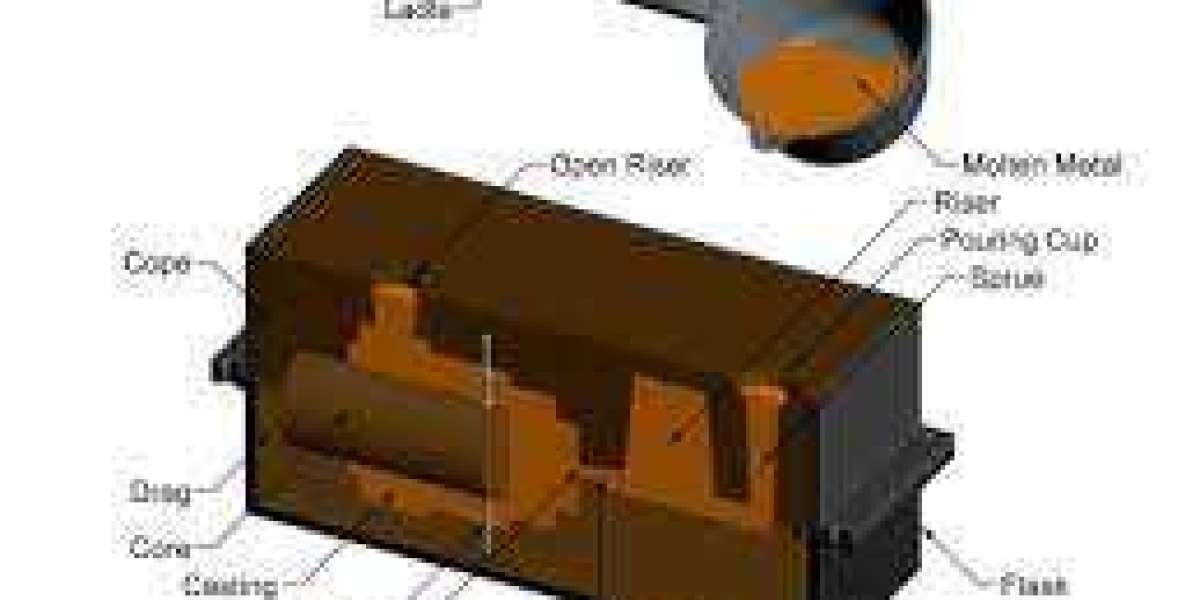
Sand casting is a manufacturing technique that involves pouring molten metal into a mold cavity formed in compacted sand. The process begins with the creation of a pattern, which is a replica of the final part to be produced. The pattern is typically made from wood, plastic, or metal and is used to create the mold cavity. The mold is then made by packing specially prepared sand around the pattern.
The Sand Casting Process:
Pattern Creation: The pattern is designed to include the desired shape and features of the final part. Skilled pattern makers create the pattern using various materials and tools. The pattern must be carefully crafted to account for factors like shrinkage and draft angles.
Mold Preparation: Once the pattern is ready, it is placed in a flask, which is a box-like frame that holds the sand during the sand casting parts process. The flask is divided into two halves, known as the cope and drag. The pattern is placed in one half, and the other half is filled with sand.
Sand Compaction: The sand casting parts in the flask is compacted around the pattern using hand rammers or mechanical vibrators. The goal is to achieve a uniform and densely packed mold cavity that accurately replicates the pattern's shape.
Pattern Removal: After the sand has been properly compacted, the pattern is removed from the mold, leaving behind a cavity in the shape of the desired part. This step requires care to prevent any damage to the mold.
Mold Assembly: The cope and drag halves are carefully aligned and joined together to create a complete mold cavity. The mold is then ready for the pouring of molten metal.
Pouring: Molten metal, typically aluminum, iron, or steel, is poured into the mold through a gating system. The gating system consists of channels and runners that distribute the molten metal evenly throughout the mold cavity.
Solidification and Cooling: Once the mold is filled with molten metal, it is allowed to cool and solidify. During this phase, the metal takes the shape of the mold cavity and solidifies into the final part.
Shakeout and Finishing: After the metal has solidified, the mold is broken apart, and the sand casting parts, also known as the "sand cast part," is removed. The casting may require additional finishing operations, such as trimming excess material, grinding, or machining, to achieve the desired specifications.
Applications of Sand Casting:
Sand casting is widely used in various industries due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness. Some common applications of sand casting include:
Automotive Industry: Sand casting is used to produce engine blocks, cylinder heads, transmission cases, and other components for automobiles. It allows for the creation of complex geometries and intricate details required in automotive parts.
Aerospace Industry: Sand casting is utilized for manufacturing critical aerospace components like turbine blades, engine casings, and structural parts. It offers the flexibility to produce parts in different alloys and provides excellent mechanical properties.
Industrial Machinery: Sand casting is employed in the production of heavy machinery components, such as pumps, valves, gears, and pulleys. Its ability to cast large parts with varying thickness makes it suitable for industrial applications.
Art and Sculpture: Artists and sculptors often use sand casting to create intricate and customized metal sculptures. The process enables the reproduction of detailed designs and offers artists a wide range of metal options.
Advantages and Limitations:
Sand casting offers several advantages, including:
Cost-Effective: Sand casting is relatively inexpensive compared to other casting methods, making it economically viable for both small-scale and large-scale production.
Versatility: The process can accommodate a wide range of part sizes, shapes, and complexities, making it suitable for diverse applications.
Design Flexibility: Sand casting allows for the creation of complex designs and detailed features that may be challenging to achieve with other casting processes.
However, sand casting also has some limitations:
Surface Finish: The surface finish of sand casting parts is not as smooth as those produced by other casting methods. Additional finishing operations are often required to achieve the desired surface quality.
Dimensional Accuracy: Achieving high dimensional accuracy can be challenging in sand casting due to factors like pattern wear, mold compaction, and metal shrinkage.
Conclusion:
Sand casting is a widely used and versatile casting process for producing metal parts. It offers numerous advantages, including cost-effectiveness, design flexibility, and the ability to cast complex geometries. Although it has some limitations, sand casting remains a popular choice in various industries, ranging from automotive and aerospace to industrial machinery and art. With ongoing advancements in materials and process control, sand casting continues to play a crucial role in modern manufacturing.