Welcome to our exploration of geomembrane sheets, a versatile and essential material in the field of civil engineering, environmental protection, and infrastructure development. In this blog post, we'll delve into the characteristics, applications, and benefits of geomembrane sheets, as well as their role in promoting sustainability and resilience in various industries.
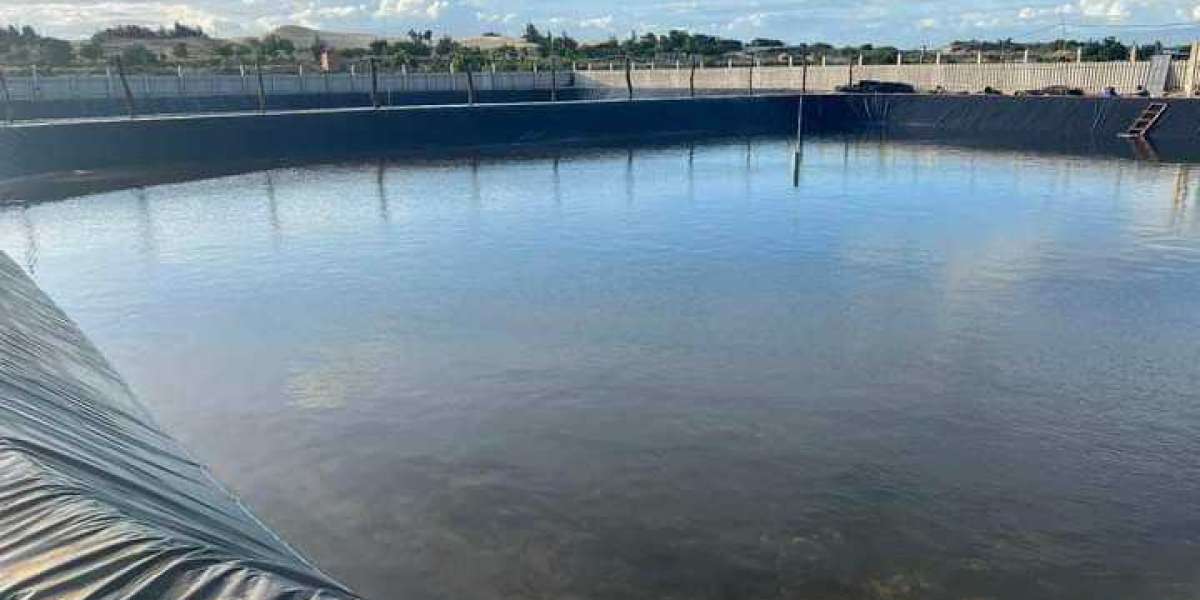
Understanding Geomembrane Sheets: Geomembrane sheets are synthetic membranes made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), or other durable materials. These flexible sheets are designed to provide impermeable barriers that prevent the seepage of liquids and gases, making them ideal for a wide range of applications where containment and environmental protection are paramount.
Applications in Civil Engineering: In the field of civil engineering, geomembrane sheets are used in various applications, including landfill liners, pond liners, canal linings, and reservoir covers. By creating impermeable barriers, geomembrane sheets prevent the leaching of contaminants into the surrounding soil and groundwater, ensuring the long-term integrity and stability of infrastructure projects.
Environmental Protection and Remediation: Geomembrane sheets play a crucial role in environmental protection and remediation efforts. They are used to line hazardous waste storage facilities, industrial containment ponds, and wastewater treatment plants, preventing the spread of pollutants and contaminants into the environment. Additionally, geomembrane sheets are used in soil remediation projects to isolate and contain contaminated soil, preventing further contamination of surrounding areas.
Water Conservation and Management: In regions facing water scarcity and drought, geomembrane sheets are used to line irrigation canals, reservoirs, and water storage tanks, reducing water loss due to seepage and evaporation. By creating impermeable barriers, geomembrane sheets help to maximize water retention and optimize water distribution, ensuring a reliable and sustainable water supply for agricultural, industrial, and municipal purposes.
Infrastructure Development and Transportation: Geomembrane sheets are also used in infrastructure development and transportation projects to improve the durability and longevity of structures. They are used as waterproofing membranes for tunnels, bridge abutments, and retaining walls, protecting against water infiltration and corrosion. Additionally, geomembrane sheets are used as erosion control barriers along highways, railways, and embankments, preventing soil erosion and slope instability.
Promoting Sustainability and Resilience: One of the key benefits of geomembrane sheets is their contribution to sustainability and resilience in various industries. By preventing the leakage of harmful substances into the environment, geomembrane sheets help to protect ecosystems, preserve natural resources, and safeguard public health. Additionally, their durability and longevity reduce the need for frequent maintenance and replacement, minimizing the environmental impact of infrastructure projects.
Enhanced Durability and Longevity: One of the most significant advancements in geomembrane technology is the development of materials and manufacturing processes that enhance durability and longevity. Modern geomembrane sheets are engineered to withstand harsh environmental conditions, including exposure to UV radiation, temperature fluctuations, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress. By incorporating additives and reinforcements, such as carbon black, antioxidants, and scrim layers, manufacturers are able to extend the service life of geomembrane sheets, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and replacement.
Improved Welding Techniques: Welding is a critical process in the installation of geomembrane liners, as it ensures the integrity and effectiveness of the containment system. Recent advancements in welding techniques, such as hot wedge welding, extrusion welding, and geoelectric welding, have revolutionized the way geomembrane liners are installed and sealed. These advanced welding techniques offer greater precision, control, and consistency, resulting in stronger and more reliable seams that minimize the risk of leaks and failures.
Smart Geomembranes and Monitoring Systems: The integration of smart technologies and monitoring systems is another exciting development in geomembrane technology. Smart geomembranes are embedded with sensors and monitoring devices that allow for real-time monitoring of environmental conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and stress. This data can be transmitted wirelessly to a central monitoring system, where it can be analyzed and used to detect potential issues, predict maintenance needs, and optimize performance. By providing early warning alerts and predictive insights, smart geomembranes help to prevent costly downtime, minimize environmental risks, and maximize operational efficiency.
Biodegradable and Eco-Friendly Materials: In response to growing concerns about plastic pollution and environmental sustainability, researchers and manufacturers are exploring the use of biodegradable and eco-friendly materials in geomembrane production. Biodegradable geomembranes are designed to break down naturally over time, reducing the long-term environmental impact of containment systems. Additionally, eco-friendly alternatives, such as recycled materials and bio-based polymers, are being developed to reduce reliance on virgin plastics and promote a circular economy approach to geomembrane manufacturing.
Customization and Tailored Solutions: Another trend in geomembrane technology is the customization and tailoring of geomembrane solutions to meet specific project requirements and environmental conditions. Manufacturers are offering a wide range of options, including different thicknesses, compositions, colors, and surface textures, to accommodate diverse applications and performance specifications. Customized geomembrane solutions enable engineers and designers to optimize performance, minimize material waste, and achieve cost-effective solutions for their projects.
Conclusion: In conclusion, geomembrane sheets are indispensable materials that play a critical role in civil engineering, environmental protection, and infrastructure development. With their impermeable barriers, they help to prevent the spread of contaminants, conserve water, enhance infrastructure durability, and promote sustainability and resilience in various industries. As we continue to face environmental challenges and strive for sustainable development, geomembrane sheets will remain essential tools for building a safer, more resilient, and more sustainable future.